오늘은 히알루론산의 여러 이점에 관해 공유해 보려고 한다. 히알루론산은 신체에서 자연적으로 생성되며 이를 사용하는 신체 부위를 균형 있게 하려면 히알루론산을 지속해서 생산해야 한다. 하지만 나이가 들어갈수록 그 생산량은 줄어든다.
하지만 다행히도 시중에서 히알루론산을 살 수 있다. 일반적으로 로션과 메이크업을 포함하는 많은 미용 제품에 이 성분이 들어 있는데, 이 다당류는 피부에만 중요한 역할을 하는 게 아니다. 사실은 관절과 뼈에도 필요하다.
히알루론산의 외부적 및 내부적 이점
젊어 보이고 싶다면 히알루론산이 새로운 방법이 될 수 있다. 히알루론산은 깨끗하고 탄력 있고 또 흠이 없는 피부에 필요한 다양한 특성을 제공해 준다.
1. 주름을 줄인다
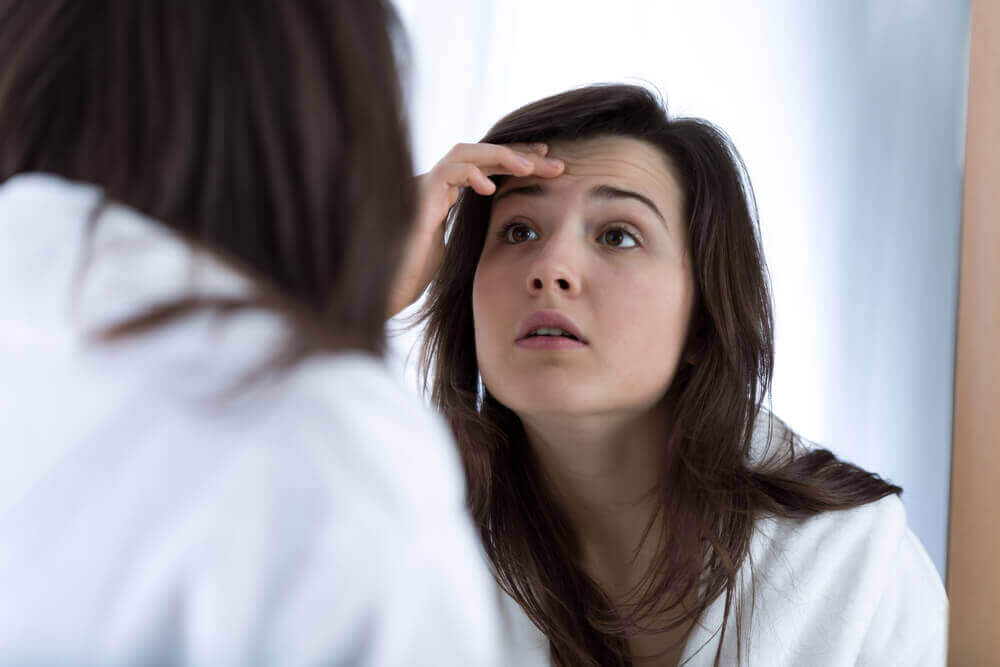

- 히알루론산은 강력한 보습제다. 콜라겐과 함께 히알루론산은 피부가 탄력을 유지하는 데 필요한 수분을 지속 시켜 준다.
- 보호 장벽을 형성하여 햇빛 및 바람과 같은 외부 요소로부터 피부를 보호해 준다.
30세가 되면 이 영양소가 함유된 로션 및 크림을 사용해야 한다.
2. 여드름과 잡티를 예방한다
히알루론산은 세포 재생 능력이 있다. 또 수분 균형을 유지하고 모공이 기름으로 막히지 않도록 해 준다. 이는 다시 말해 여드름이 적고 어려 보인다는 뜻이기도 하다.
매일 새로운 제품이 출시되어 전 세계 뷰티 센터에서 테스트되고 있다. 이처럼 이상하게 들릴 수도 있지만, 히알루론산은 피부에 좋을 뿐만 아니라 눈, 입술, 잇몸 및 머리카락에도 아주 좋다.
더 읽어보기: 자연적인 방법으로 피부 잡티를 치유해 보자
3. 눈을 건강하게 한다
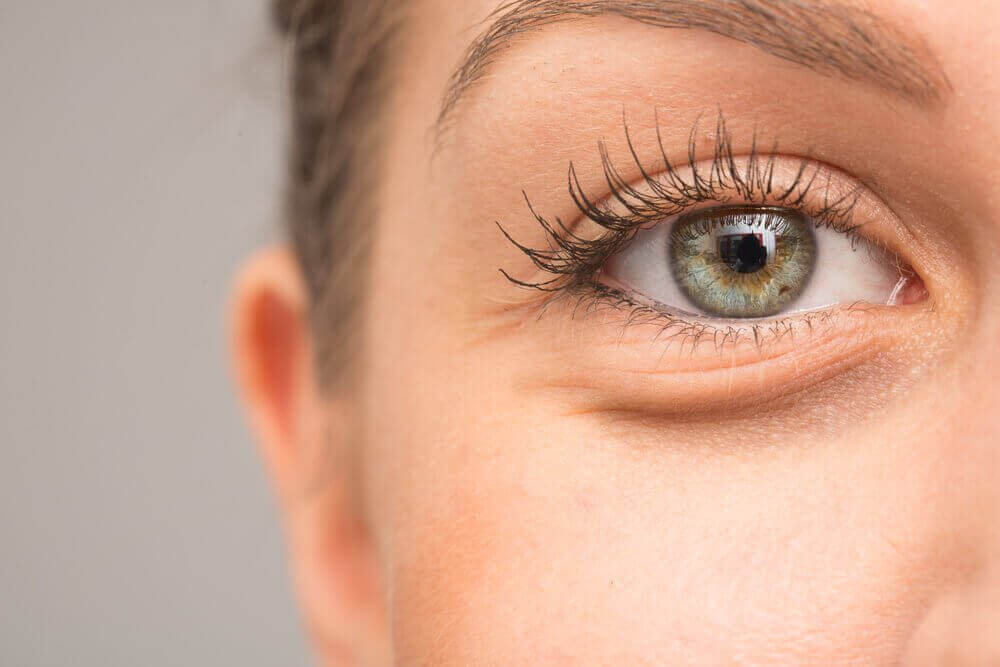

히알루론산은 눈을 촉촉하게 유지해 주고 영양소의 운반을 용이하게 하며 눈의 유리액을 통해 윤활유 역할을 한다. 이는 좋은 시력, 특히 수술을 받을 때 필요하다. 실제로 의사들은 눈이 건조하면 안 된다고 항상 강조한다.
4. 입술에 볼륨감을 준다
이 모이스처라이저를 입술에 바르면 입술이 탄탄하게 유지된다. 실제로 여성이 히알루론산 립 트리트먼트를 사용했는지 여부는 쉽게 파악할 수 있다. 입술이 꽤 관능적으로 보이기 시작하기 때문이다. 통통한 입술을 얻는 건 일시적이지만, 매우 안전한 방법이다.
5. 잇몸을 강화한다
히알루론산은 인대를 강화하고 잇몸이 입 전체를 지탱할 수 있도록 한다. 그리고 결합 조직을 수화 시켜 치아와 뼈 사이의 연결을 강화한다. 다시 말해, 구강 건강을 유지하는 데 있어 히알루론산의 존재가 필수적이라고 할 수 있다.
더 읽어보기: 잇몸 출혈의 원인과 예방
6. 모발을 강화한다
이 특별한 영양소는 모발을 활성화한다. 그리고 갈라진 끝을 개선하여 모발을 밝고 강하게 만들어준다. 히알루론산은 손상된 모발을 보습하고 복구해주는 모든 종류의 제품에 들어 있다.
7. 뼈를 보호하고 관절 윤활제로 작용한다
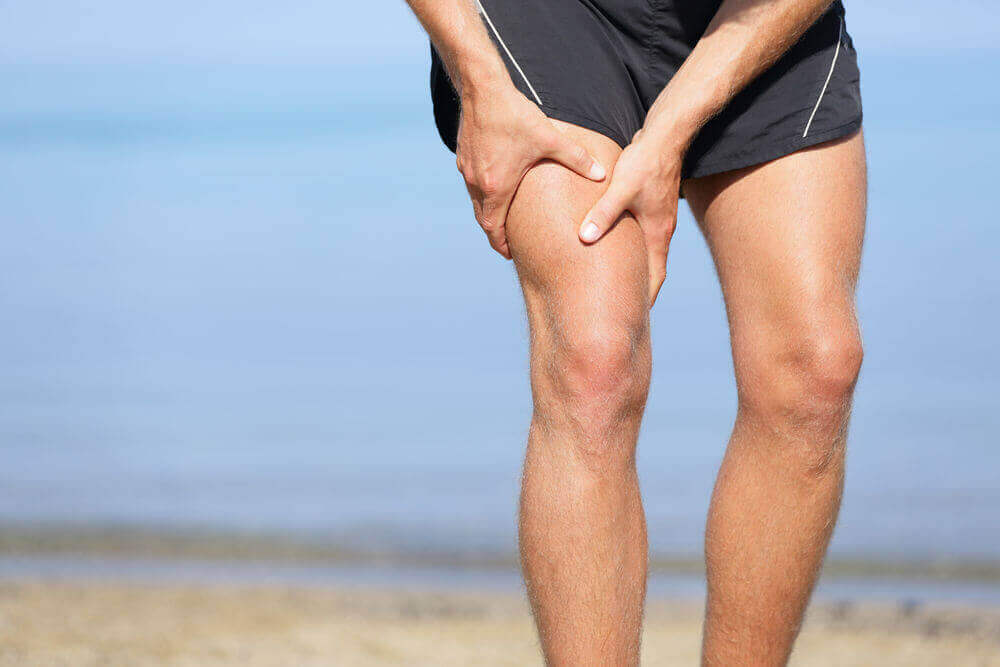

뼈를 정말로 보호하고 싶다면 젤 같은 커버가 있어야 한다. 무릎, 팔꿈치 및 신체의 모든 관절에 필요하므로 운동선수에게 매우 권장된다.
히알루론산은 기본적으로 마찰을 줄이고 통증이나 부상 없이 움직일 수 있게 해준다. 실제로 특정 스포츠는 관절염의 위험을 증가시킬 수 있으며 히알루론산 보충제는 그것을 치료하는 데 도움이 될 수 있다.
노인들과 운동선수들은 모두 관절을 윤활하게 하기 위해 그것을 사용한다.
요약하자면, 히알루론산은 제대로 기능하는 신체에 있어 기본이라고 할 수 있다. 따라서 젊고 건강해 지려면 반드시 히알루론산이 필요하다.
참고 문헌
모든 인용된 출처는 품질, 신뢰성, 관련성 및 유효성을 보장하기 위해 저희 팀이 철저히 검토했습니다. 이 글의 참고 문헌은 신뢰할 수 있으며 학문적 또는 과학적 정확성을 갖춘 것으로 간주되었습니다.
- Boira, C., Essendoubi, M., Meunier, M., Lambert, C., Auriol, D., Manfait, M., Piot, O., Scandolera, A., & Reynaud, R. (2024). Hyaluronic acid: elucidating its penetration into, and effect on hair fibers using confocal Raman spectroscopy and biometric techniques. Journal Of Physical Chemistry & Biophysics. https://www.preprints.org/manuscript/202401.1325/v1
- Bravo, B., Correia, P., Gonçalves Junior, J., Sant’Anna, B., & Kerob, D. (2022). Benefits of topical hyaluronic acid for skin quality and signs of skin aging: From literature review to clinical evidence. Dermatologic therapy, 35(12). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10078143/
- Bukhari, S., Roswandi, N., Waqas, M., Habib, H., Hussain, F., Khan, S., Sohail, M., Ramli, N., Thu, H., & Hussain, Z. (2018). Hyaluronic acid, a promising skin rejuvenating biomedicine: A review of recent updates and pre-clinical and clinical investigations on cosmetic and nutricosmetic effects. International Journal Of Biological Macromolecules, 120, 1682-1695. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S014181301833770X
- Dahiya, P., & Kamal, R. (2013). Hyaluronic Acid: a boon in periodontal therapy. North American Journal of Medical Sciences, 5(5), 309–315. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3690787/
- Desmawati, D., & Sulastri, D. (2019). Phytoestrogens and Their Health Effect. Open access Macedonian journal of medical sciences, 7(3), 495–499. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6390141/
- Fogagnolo, P., Romano, D., De Ruvo, V., Sabella, P., & Rossetti, L. (2022). Clinical Efficacy of an Eyedrop Containing Hyaluronic Acid and Ginkgo Biloba in the Management of Dry Eye Disease Induced by Cataract Surgery. Journal of ocular pharmacology and therapeutics : the official journal of the Association for Ocular Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 38(4), 305–310. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35442771/
- Frenkel J. (2014). The role of hyaluronan in wound healing. International wound journal, 11(2), 159–163. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7950635/
- Gupta, R., Lall, R., Srivastava, A., & Sinha, A. (2019). Hyaluronic Acid: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Trajectory. Frontiers in veterinary science, 6, 192. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6603175/
- Halachmi, S., Ben Amitai, D., & Lapidoth, M. (2013). Treatment of acne scars with hyaluronic acid: an improved approach. Journal of drugs in dermatology : JDD, 12(7). https://jddonline.com/articles/treatment-of-acne-scars-with-hyaluronic-acid-an-improved-approach-S1545961613P0121X
- Hwang, H., & Lee, C. (2023). Recent progress in hyaluronic-acid-based hydrogels for bone tissue engineering. Gels, 9(7), 588. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10379028/
- Jensen, G., Attridge, V., Lenninger, M., & Benson, K. (2015). Oral intake of a liquid high-molecular-weight hyaluronan associated with relief of chronic pain and reduced use of pain medication: results of a randomized, placebo-controlled double-blind pilot study. Journal of medicinal food, 18(1), 95–101. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25415767/
- Jung, Y., Hwang, C., Ha, J., Choi, D., Sohn, K., Lee, Y., Seo, Y., Lee, Y., Kim, C., Lee, J., & Im, M. (2017). Hyaluronic Acid Decreases Lipid Synthesis in Sebaceous Glands. The Journal of investigative dermatology, 137(6), 1215–1222. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28163068/
- Litwiniuk, M., Krejner, A., Speyrer, M., Gauto, A., & Grzela, T. (2016). Hyaluronic acid in inflammation and tissue regeneration. Wounds, 28(3), 78-88. https://www.hmpgloballearningnetwork.com/site/wounds/article/hyaluronic-acid-inflammation-and-tissue-regeneration
- Ma, J., Granton, P., Holdsworth, D., & Turley, E. (2013). Oral administration of hyaluronan reduces bone turnover in ovariectomized rats. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 61(2), 339–345. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23256527/
- Maulvi, F., Shaikh, A., Lakdawala, D., Desai, A., Pandya, M., Singhania, S., Vaidya, R., Ranch, K., Vyas, B., & Shah, D. (2017). Design and optimization of a novel implantation technology in contact lenses for the treatment of dry eye syndrome: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Acta biomaterialia, 53, 211–221. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28131945/
- Maulvi, F., Soni, T., & Shah, D. (2015). Extended release of hyaluronic acid from hydrogel contact lenses for dry eye syndrome. Journal of biomaterials science. Polymer edition, 26(15), 1035–1050. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26176811/
- Mehta, V., Kaçani, G., Moaleem, M., Almohammadi, A., Alwafi, M., Mulla, A., Alharbi, S., Aljayyar, A., Qeli, E., Toti, Ç., Meto, A., & Fiorillo, L. (2022). Hyaluronic Acid: A New Approach for the Treatment of Gingival Recession-A Systematic Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(21). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9658310/
- Liu, K. (2020). The hype on hyaluronic acid. Harvard Health Publishing. Consultado el 18 de junio del 2024 https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/the-hype-on-hyaluronic-acid-2020012318653
- Oe, M., Tashiro, T., Yoshida, H., Nishiyama, H., Masuda, Y., Maruyama, K., Koikeda, T., Maruya, R., & Fukui, N. (2016). Oral hyaluronan relieves knee pain: a review. Nutrition journal, 15, 11. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4729158/
- Palmieri, B., Merighi, A., Corbascio, D., Rottigni, V., Fistetto, G., & Esposito, A. (2013). Fixed combination of hyaluronic acid and chondroitin-sulphate oral formulation in a randomized double blind, placebo controlled study for the treatment of symptoms in patients with non-erosive gastroesophageal reflux. European review for medical and pharmacological sciences, 17(24), 3272–3278. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24379055/
- Pereira, T., Jüni, P., Saadat, P., Xing, D., Yao, L., Bobos, P., Agarwal, A., Hincapié, C., & da Costa, B. (2022). Viscosupplementation for knee osteoarthritis: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ (Clinical research ed.), 378, e069722. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36333100/
- Pinto, J., López, A., Blázquez, F., Urbano, R., & González, M. (2017). Efficacy and Safety of 0.2% Hyaluronic Acid in the Management of Dry Eye Disease. Eye & contact lens, 43(1), 57–63. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26783978/
- Savarino, V., Pace, F., Scarpignato, C., Esoxx Study Group, Astegiano, M., Calabrese, C., … & Segato, S. (2017). Randomised clinical trial: mucosal protection combined with acid suppression in the treatment of non‐erosive reflux disease–efficacy of Esoxx, a hyaluronic acid–chondroitin sulphate based bioadhesive formulation. Alimentary pharmacology & therapeutics, 45(5), 631-642. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5347926/
- Sundaram, H., Mackiewicz, N., Burton, E., Peno-Mazzarino, L., Lati, E., & Meunier, S. (2016). Pilot Comparative Study of the Topical Action of a Novel, Crosslinked Resilient Hyaluronic Acid on Skin Hydration and Barrier Function in a Dynamic, Three-Dimensional Human Explant Model. Journal of drugs in dermatology: JDD, 15(4), 434–441. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27050698/
- Yang, Y., Lee, W., Kim, Y., & Hong, Y. (2021). A Meta-Analysis of the Efficacy of Hyaluronic Acid Eye Drops for the Treatment of Dry Eye Syndrome. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(5), 2383. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7967738/